
The beginner’s guide to the circular economy
The technical cycle of the butterfly diagram Published on 23 May 2022 On the right-hand side of the butterfly diagram is the technical cycle, relevant for products that are used rather than consumed.

Circular economy — Urbaser
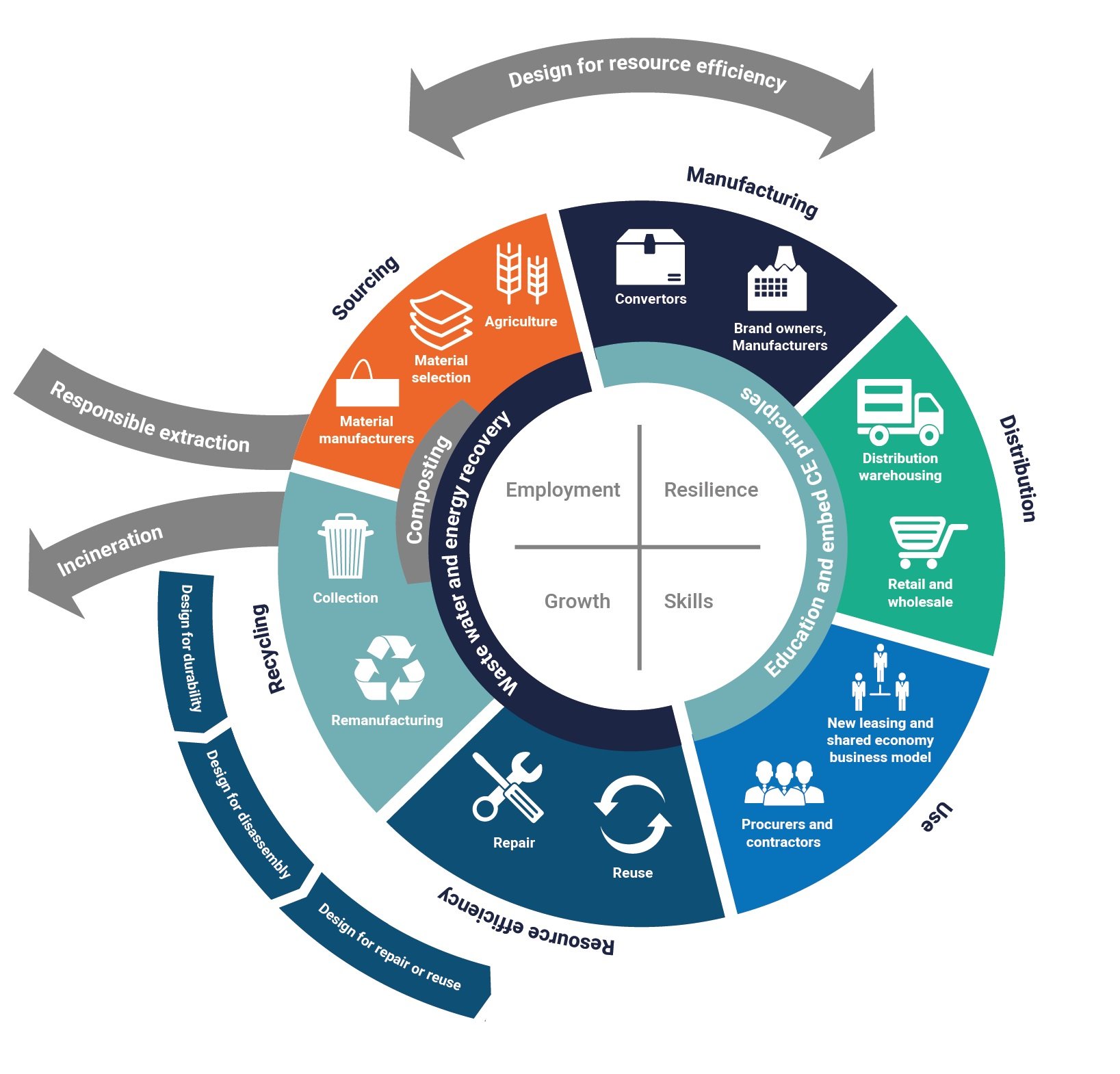
The circular economy system diagram, known as the butterfly diagram, illustrates the continuous flow of materials in a circular economycircular economy A systems solution framework that tackles global challenges like climate change, biodiversity loss, waste, and pollution.
Buying Circles The Opportunity for Procurement in the Circular Economy
This diagram demonstrates how each stage of a product can use recycled or reused materials to manage resources better. The circular economy butterfly diagram by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation illustrates how we can minimize waste using both renewable and non-renewable materials. © Ellen MacArthur Foundation, Fair Use
How Does The Circular Flow Of Economy Eliminate Waste?
Introduction to Circular Economy for a Sustainable Built Environment The Ellen MacArthur Foundation was one of the pioneers in promoting the Circular Economy. The theoretical framework that we use for explaining the Circular Built Environment in this course is based on its principles.

Circular Economy City of Adelaide
1.2.3 Circular Economy System Diagram. Below you see the Ellen MacArthur Foundation's "butterfly diagram". The Diagram illustrates the concept behind a Circular Economy model, and highlights the continuous flow of biological and technical materials through the "value circle". In this course we will focus on the right side of the.
What is Circular Economy & How Does It Work? Complete Guide RTS Recycle Track Systems
Published on 12 February 2021. There's a world of opportunity to re-think and re-design the way we make things in a circular economy. 'Re-Thinking Progress' explores how through a change in perspective we can re-design the way our economy works - designing products that can be 'made to be made again' and powering the system with renewable.
What Is Circular Economy, And How Does It Help Environment?
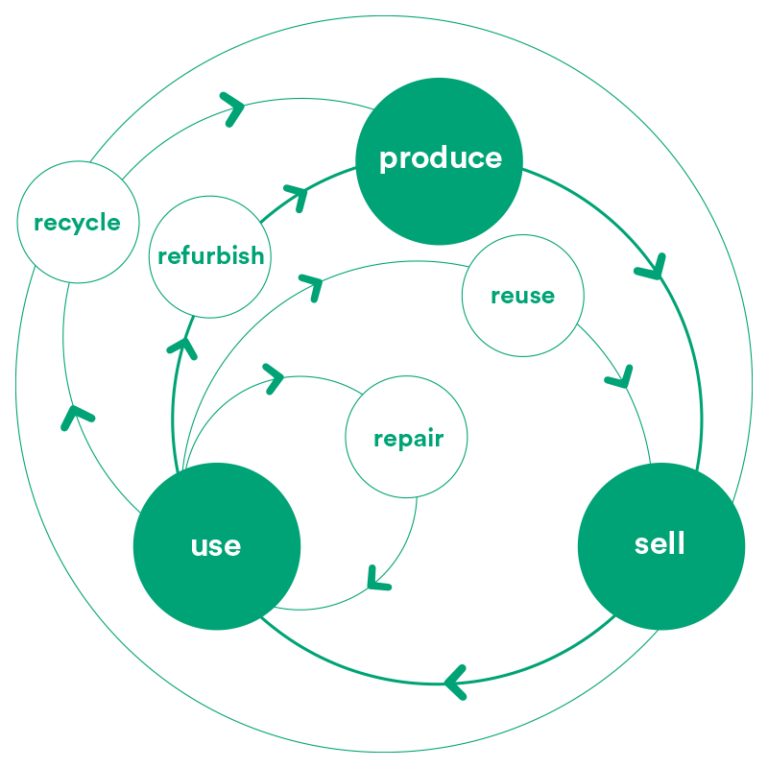
The two ideas are related, but a circular economy is more systemic and ambitious. Most recyclable products in the linear economy can only be downcycled, meaning they lose quality for each new life.

Sustainability Material Challenge Lab AB Circular economy, Economy design, Biochemical
The Butterfly Diagram accentuates the continuous flow of materials in the circular economy. Its ambition is to showcase the difference between technical and organic cycles through their 'value circles'.
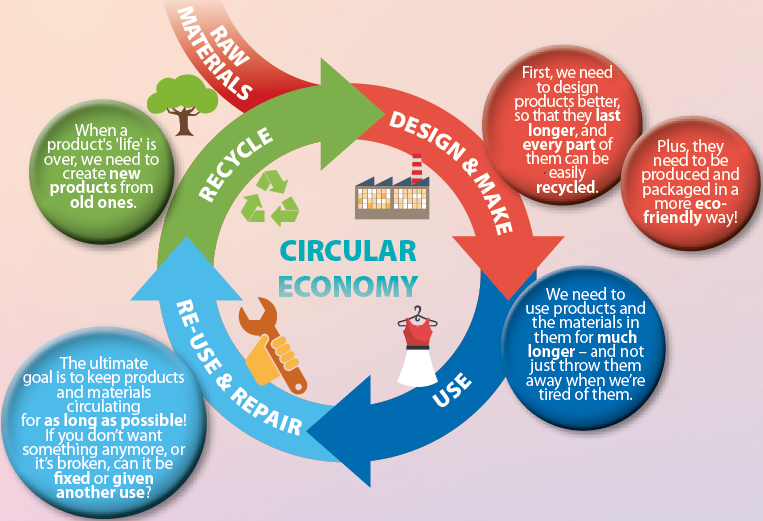
All about the circular economy National Geographic Kids
Look at the diagram below. It shows a big-picture view of how the circular economy works. There are 2 material cycles. Biological materials on the left, technical materials on the right. These two cycles look like the wings of a butterfly, which is why the diagram is often affectionately known as the Butterfly Diagram. Let's explore them in turn.

Why the circular economy is the business opportunity of our time Institute for Career Studies
The 'butterfly diagram' shows the continuous flow of materials in a circular economy. Circular economy explained Explaining the circular economy: re-thinking progress Watch our beginner's guide to understanding how a circular economy works. Circular economy explained Circular economy key ideas
Scheme for a circular economy cycle. Download Scientific Diagram
The Butterfly Diagram is a powerful tool that helps us to understand the application of the Circular Economy model in practice. In a single image, we have a holistic view of the main assumptions of the model, the proposed changes, and the several solutions that facilitate the transition.

Circular Economy WikiWaste
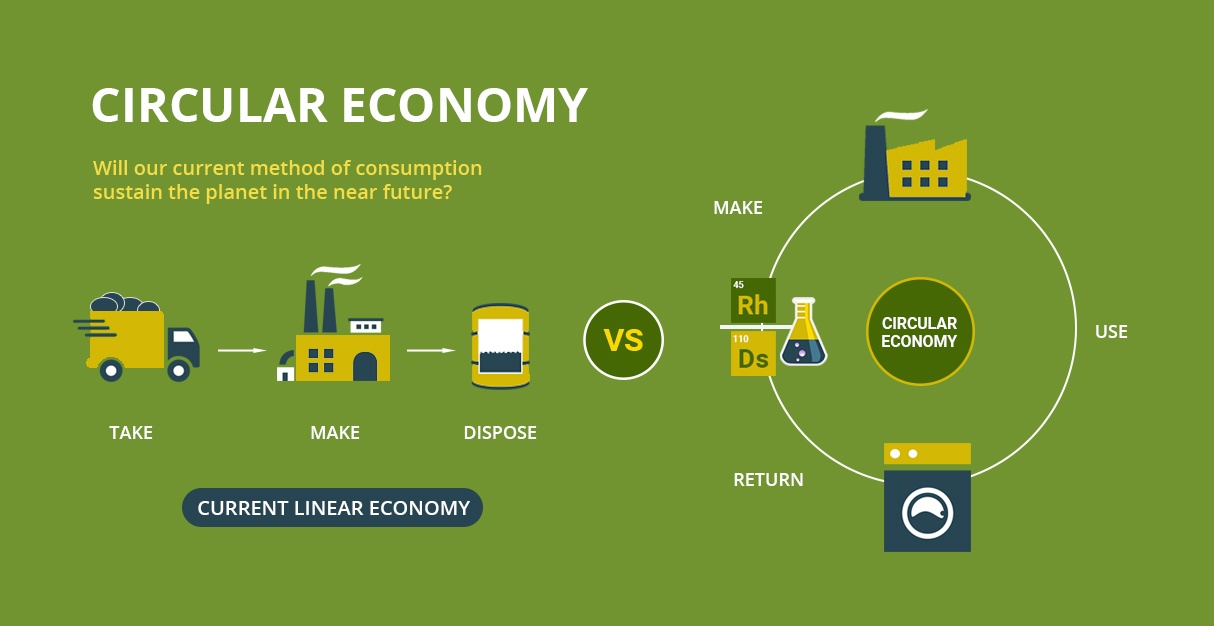
A circular economy is a system that preserves resources by reusing and repurposing existing products and/or the materials used in making them, rather than manufacturing and consuming new ones. Ultimately, that will help us regenerate our natural ecology so it can sustain future generations, benefiting people and the planet..
The Circular Economy What it means for Fracking and Plastic FracTracker Alliance
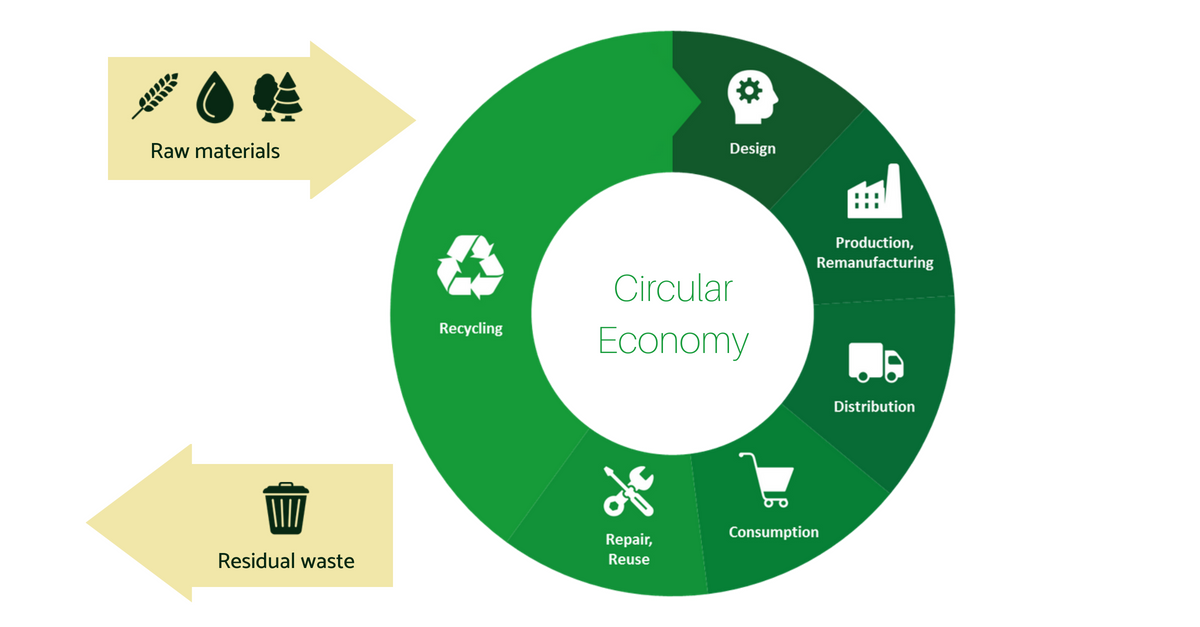
1. Designs out waste and pollution Circular economy designs out economic activities that negatively impact human health and natural systems. This includes the release of greenhouse gases, all types of pollution and traffic congestion. 2. Keeps products and materials in use

The Circular Economy Vision, Problems and Smart City Solutions
The circular economy diagram, or the "butterfly" diagram as it's also called, is a key illustration that helps explain the circular economy. Divided into two halves — the biological cycle and the technical cycle — the diagram shows an ideal flow of materials and products through the economy.
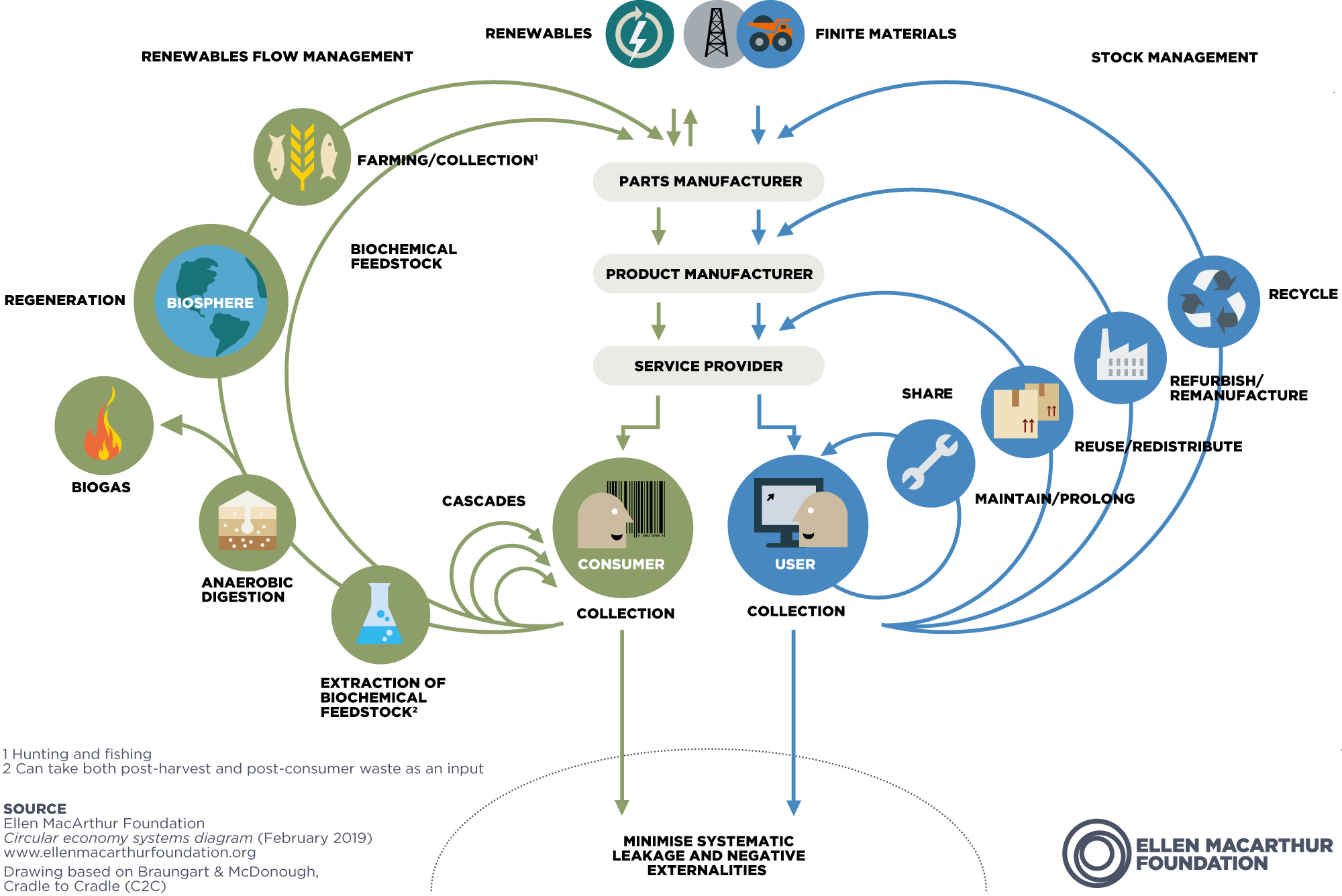
The Circular Economy In Detail
A circular economy reduces material use, redesigns materials and products to be less resource intensive, and recaptures "waste" as a resource to manufacture new materials and products. Circularity is embraced within the sustainable materials management (SMM) approach that EPA and other federal agencies have pursued since 2009.
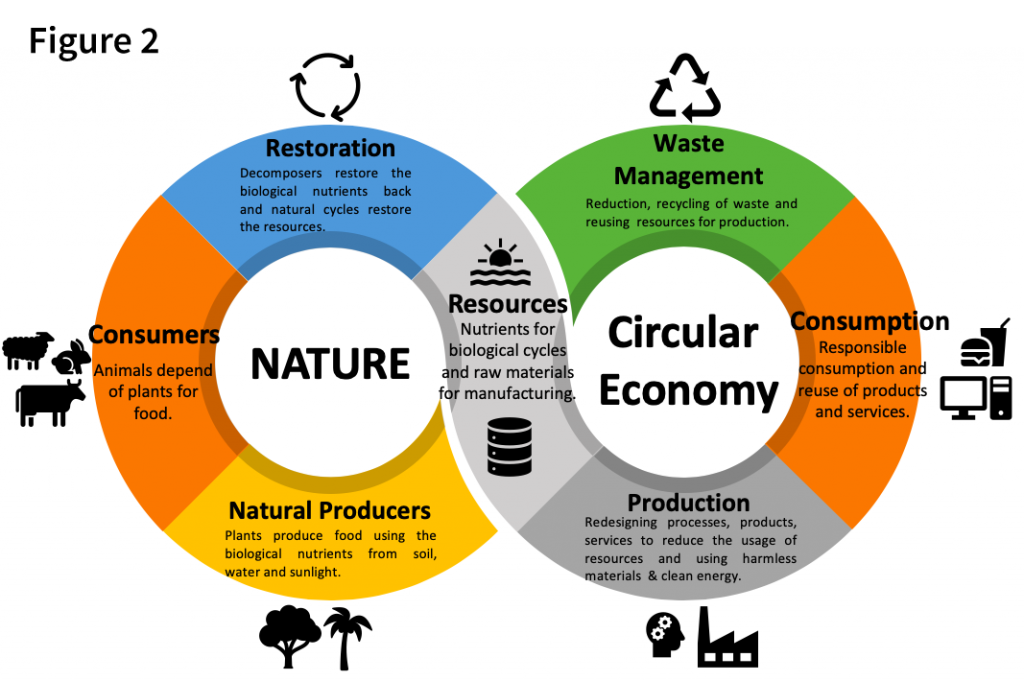
Circular Economy, Sustainability and Business Opportunities The European Business Review
5 and Sustainability [see Geissdoerfer et al., 2017, Figure 3: 762 for the full list]). In 2001 the International Society for Industrial Ecology (ISIE) was founded. Yet despite the early articulation of circular economy principles as cited above, and a detailed discussion of the concept in a well-known environmental